1. 传统多列浮动
- 各列固定宽度,并且左浮动;
- 一列中的数据块为一组,列中的每块依次排列;
- 更多数据加载时,需要分别插入到不同的列中。
|
|
- 优点:布局简单,应该说没啥特别的难点;不用明确知道数据块高度,当数据块中有图片时,就不需要指定图片高度。
- 缺点:列数固定,扩展不易,当浏览器窗口大小变化时,只能固定的x列,如果要添加一列,很难调整数据块的排列;滚动加载更多数据时,还要指定插入到第几列中,还是不方便。
2. CSS3 样式定义
|
|
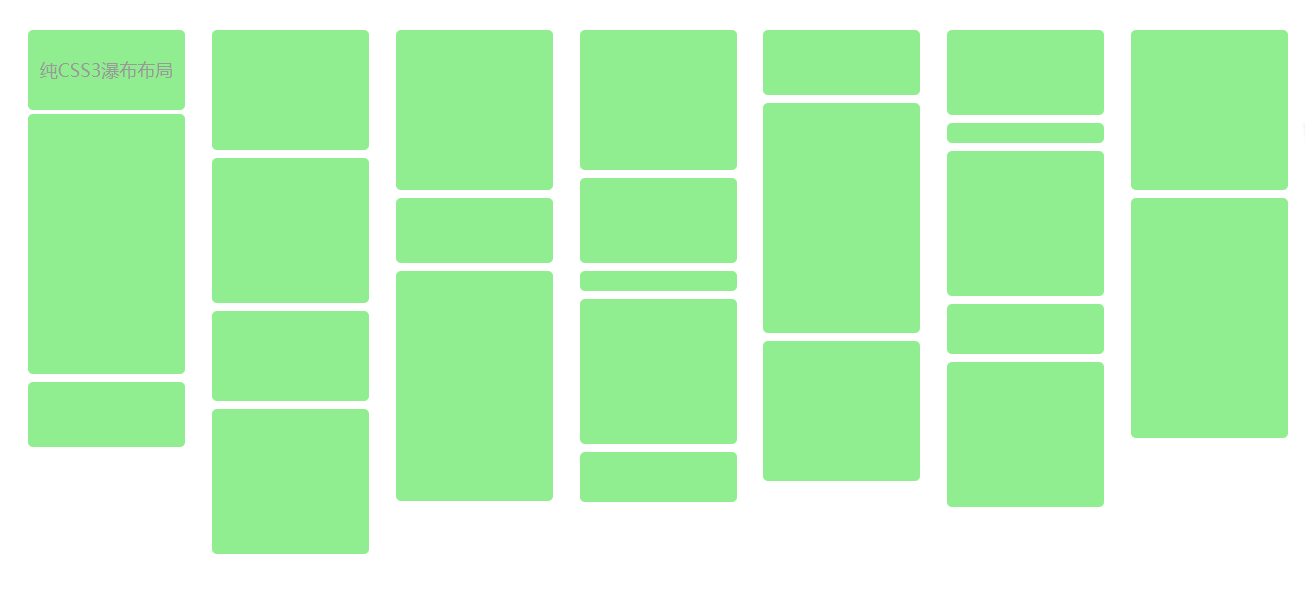

- 优点:直接 CSS 定义,最方便了;扩展方便,直接往容器里添加内容即可。
- 缺点:只有高级浏览器中才能使用;还有一个缺点,他的数据块排列是从上到下排列到一定高度后,再把剩余元素依次添加到下一列,这个本质上就不一样了;
鉴于这两个主要缺点,注定了该方法只能局限于高端浏览器,而且,更适合于文字多栏排列。
3. 绝对定位
思路:
- 数据块排列(对容器中已有元素进行排列),算法步骤简述下:
设置(块元素宽度一致)
- 初始化时,对容器中已有数据块元素进行第一次计算,需要用户给定: a,容器元素 — 以此获取窗口总宽度; b,列宽度(块元素宽度); c,最小列数;
- 计算显示列数:窗口宽度除以一个块框宽度向下取整,并设置waterfall显示的居中
- 存储每列的高度
- 获得列数后,需要保存每个列的当前高度,这样在添加每个数据块时,才知道起始高度是多少;
- 依次取容器中的所有数据块,先寻找当前高度最小的某列,之后根据列序号,确定数据块的left,top值,left 为所在列的序号乘以列宽,top 为所在列的当前高度,最后更新所在列的当前高度加上这个数据块元素的高度,至此,插入一个元素结束;
- 当所有元素插入完毕后,调整容器的高度为各列最大的高度值,结束依次调整。
- 异步加载数据,包含两个步骤:
- 绑定滚动事件,并确定预加载线高度值,即滚动到哪个高度后,需要去加载数据,其实这个就是列的最小高度值,这样当前滚动值和最小高度值比较一下即可判断出来,是否要触发加载数据;
- 加载数据,函数传参,能提供加载数据函数和停止加载(加载多少时停止)函数,以更方便的控制。
- 优点:最优的一种方案,方便添加数据内容,窗口变化,列数/数据块都会自动调整;方便添加数据内容,窗口变化,列数/数据块都会自动调整;
- 缺点:需要实现知道数据块高度,如果其中包含图片,需要知道图片高度;JS 动态计算数据块位置,当窗口缩放频繁,可能会狂耗性能。

